Share your photos by tagging us and using the hashtag #BigGreenEgg.
Want to see how the EGG is made? Click to Watch
OT - What are you doing right now?
Comments
-
My sugar going up 25% in 2022. Used to be able to book for a year, now they’re only allowing me to book for 3 months out. I use 2,000# a week on averagealaskanassasin said:we fertilize corn with anhydrous ammonia , 2021 it was $575 a ton, next year they are guessing it will be between $1,200-$1,500 a ton -
I tried to pre pay for ammonia… not a optionSouth of Columbus, Ohio.
-
-
Got my booster. Need the flu still.______________________________________________I love lamp..
-
Got my booster, the flu and pneumonia (second) at the same time. I don't recommend doing that in the future.XL and Small BGEs in South Carolina
-
 Made a quick lunch. Reheated collards, with chili water added, topped with 2 lightly poached eggs.
Made a quick lunch. Reheated collards, with chili water added, topped with 2 lightly poached eggs.LBGE
Pikesville, MD
-
Locally here they were locking in prices until December 31, then any prepay money is just credit against what it costs at delivery. Lot of anhydrous went down the last couple weeks as guys had pre-payed in July/August at the <$1000/ton range.alaskanassasin said:I tried to pre pay for ammonia… not a option -
Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )
______________________________________________I love lamp.. -
(trolling is fun!)
______________________________________________I love lamp.. -
-
I think they should go back to plowing.nolaegghead said:Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )
Location- Just "this side" of Biloxi, Ms.
Status- Standing by.
The greatest barrier against all wisdom, the stronghold against knowledge itself, is the single thought, in ones mind, that they already have it all figured out. -
nolaegghead said:
Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )
but what if i wanted to grow plankton in a 995 billion gallon tank to feed some fishes
fukahwee maineyou can lead a fish to water but you can not make him drink it -
It's common here to plant a nitrogen fixer between wheat crops, direct drill into the remaining stubble.nolaegghead said:Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management ) -
I think we have a resident expert here on a big category of nitrogen fixing bean crops.... @Legume ?Eoin said:
It's common here to plant a nitrogen fixer between wheat crops, direct drill into the remaining stubble.nolaegghead said:Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )
______________________________________________I love lamp.. -
I’ve never tried fall application of Anhydrous, I’m chicken I guess but stability is a concern and if we have a disaster spring, being able to get the corn planted where you planning on putting it maybe a challenge. As far as the price of fertilizer I’ll just eat it. It’s always something in farming. Smart money probably has 28 in tanks on the farm ready for the springFarmingPhD said:
Locally here they were locking in prices until December 31, then any prepay money is just credit against what it costs at delivery. Lot of anhydrous went down the last couple weeks as guys had pre-payed in July/August at the <$1000/ton range.alaskanassasin said:I tried to pre pay for ammonia… not a optionSouth of Columbus, Ohio. -
Don’t forget @PigBeanUs. I understand he farms beans in the U.S. And pigs too.nolaegghead said:
I think we have a resident expert here on a big category of nitrogen fixing bean crops.... @Legume ?Eoin said:
It's common here to plant a nitrogen fixer between wheat crops, direct drill into the remaining stubble.nolaegghead said:Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management ) -
Scored 2 boxes of 22-250 ammo today. It’s the only 2 boxes I have seen on the shelves in a year and a half. I wish they would of had 200 boxes.

Location- Just "this side" of Biloxi, Ms.
Status- Standing by.
The greatest barrier against all wisdom, the stronghold against knowledge itself, is the single thought, in ones mind, that they already have it all figured out. -
Ammonia production is pegged to the cost of natural gas. The global price for LNG has shot up between 250-400%, which has caused the price of ammonia to skyrocket. This happened before as recently as 2018.
______________________________________________I love lamp.. -
This! Got home made chicken tenders in the oven and eggplant parm. Gonna be a good dinner

-
**** why is the pic sidways?
-
The sideways pics started around a year ago. I still have no idea why they started turning sideways.ValleyGirl said:**** why is the pic sidways?Location- Just "this side" of Biloxi, Ms.
Status- Standing by.
The greatest barrier against all wisdom, the stronghold against knowledge itself, is the single thought, in ones mind, that they already have it all figured out. -
@Botch had a slow loading internet connection. He got the Buffalo to fix that, but they broke the rest.SGH said:
The sideways pics started around a year ago. I still have no idea why they started turning sideways.ValleyGirl said:**** why is the pic sidways?I would rather light a candle than curse your darkness.
-
-
nolaegghead said:
Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )
Get a haircut.
South of Columbus, Ohio. -
nolaegghead said:Ammonia production is pegged to the cost of natural gas. The global price for LNG has shot up between 250-400%, which has caused the price of ammonia to skyrocket. This happened before as recently as 2018.
Pegged is a strong word, unless natural gas has doubled in 6 months, I am pretty sure they are just sticking it to farmers because......... they can. Crop prices are up and everyone has their hand out.
South of Columbus, Ohio. -
“Did someone say aNus?” - Scottie, probablynolaegghead said:Understanding the relationship between nitrogen (N) and crop rotation is very important when making N management decisions. There are several benefits to using crop rotation, including improved nutrient cycling, soil tilth, and soil physical properties; and enhanced weed control. Crop rotation also may influence the rate of N mineralization or the conversion of organic N to mineral N by modifying soil moisture, soil temperature, pH, plant residue, and tillage practices.
The incremental increase in N use over the past five decades, due to emphasis on maximizing yield, has led to a subsequent increase in N in the soil profile of some agricultural fields. Therefore, the influence of agricultural practices on water quality has prompted studies to develop best management practices to optimize the use of fertilizer N and reduce N loss to surface and groundwater. Crop rotation can play a major role in minimizing the potential risk of nitrate leaching to surface and groundwater by enhancing soil N availability, reducing the amount of N fertilizer applied, and minimizing the potential risk of N leaching.
Research on the impact of long-term crop rotation on soil N availability shows that planting alfalfa, corn, oat, and soybean significantly increased the mineralized net N in soil compared with planting continuous corn. Because soil N mineralization can effect yield, crop rotation thus can be used as a management system to enhance the soil nutrient pool, thereby reducing the fertilizer N input and minimizing the risk of leaching of excess N during wet weather.
A combination of conservation tillage practices and crop rotation has been shown to be very effective in improving soil physical properties. Long-term studies in the Midwest indicate that corn-soybean rotation improves yield potential of no-till compared with continuous corn. The reduction in yield of continuous corn in no-till is attributed to low soil temperature during seed germination, which is evident on poorly drained soils under no-till. Studies show that the poor performance of no-till corn following corn is more likely due to the previous crop than to surface residue conditions preventing early-season warming and drying of soils.
The use of a legume cover in crop rotation can provide a substantial amount of N to a succeeding crop. Research has indicated that seeding rates for legumes can be reduced by approximately one-third of that recommended for forage production when used as cover crops without sacrificing biomass or N accumulation. Also, the type of crop grown in the previous year can impact the efficiency of conservation tillage, especially for no-till systems, due to the kind and amount of crop residue from the previous crop.
(from https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/value-crop-rotation-nitrogen-management )"I've made a note never to piss you two off." - Stike
"The truth is, these are not very bright guys, and things got out of hand." - Deep Throat -
Anyone hungry for some delicious 3d printed vegetarian steak?
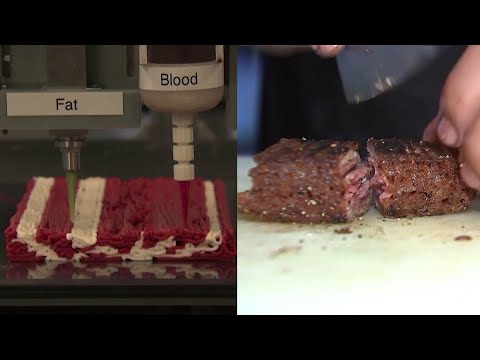 https://youtu.be/tXksi9gynQE
https://youtu.be/tXksi9gynQE
Me neither."The pig is an amazing animal. You feed a pig an apple and it makes bacon. Let's see Michael Phelps do that" - Jim Gaffigan
Minnesota -
Just ordered a new pair of barn boots and some fresh overalls 👍
Location- Just "this side" of Biloxi, Ms.
Status- Standing by.
The greatest barrier against all wisdom, the stronghold against knowledge itself, is the single thought, in ones mind, that they already have it all figured out. -
It's funny but in that recent Marc Maron podcast with David Chang, David mentioned trying some synthetic meat that was really good and that he said he couldn't tell the difference from the real thing.WeberWho said:Anyone hungry for some delicious 3d printed vegetarian steak? https://youtu.be/tXksi9gynQE
https://youtu.be/tXksi9gynQE
Me neither.
He might also talk about it on his new show that's on Hulu, I'm not sure."I've made a note never to piss you two off." - Stike
"The truth is, these are not very bright guys, and things got out of hand." - Deep Throat -
Just saw the following and thought to myself that there exists perhaps no single greater summation of @sgh’s passions…

Categories
- All Categories
- 184.1K EggHead Forum
- 16.1K Forum List
- 461 EGGtoberfest
- 1.9K Forum Feedback
- 10.5K Off Topic
- 2.4K EGG Table Forum
- 1 Rules & Disclaimer
- 9.2K Cookbook
- 16 Valentines Day
- 118 Holiday Recipes
- 348 Appetizers
- 521 Baking
- 2.5K Beef
- 90 Desserts
- 167 Lamb
- 2.4K Pork
- 1.5K Poultry
- 33 Salads and Dressings
- 322 Sauces, Rubs, Marinades
- 548 Seafood
- 175 Sides
- 122 Soups, Stews, Chilis
- 44 Vegetarian
- 103 Vegetables
- 315 Health
- 293 Weight Loss Forum













